Powder Laser Energy Deposition (ED)
Additive Manufacturing based on established welding technology
Powder Laser Energy Deposition (ED), also known as Laser Metal Deposition (LMD) is a welding technology used for many years. Recently the technology is adopted as an Additive Manufacturing technology by system integrators and off-the-shelf system providers. In this section you learn about the background of Powder Laser ED.
Technology principle
How does Powder Laser Energy Deposition work?
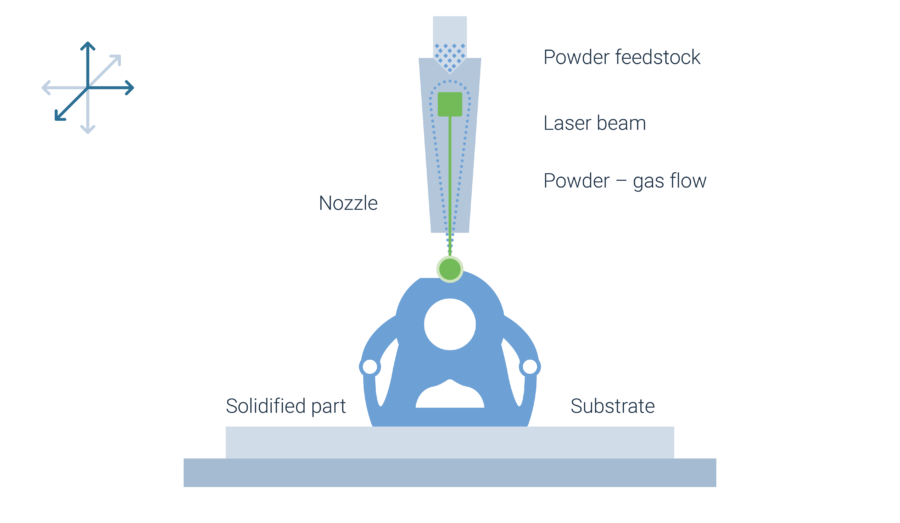
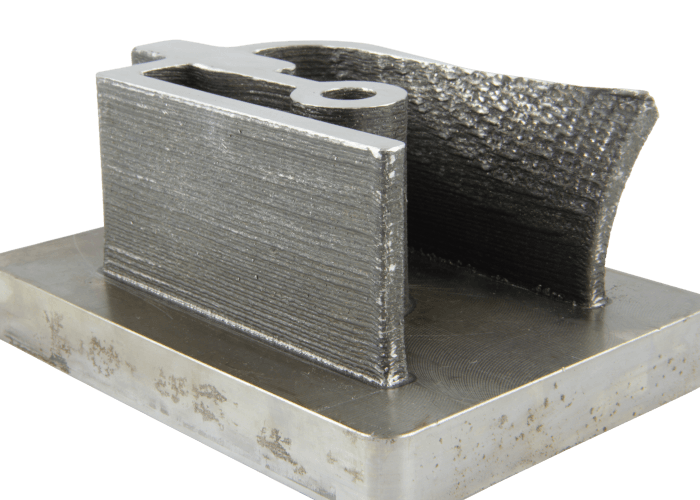
Powder Laser ED, also sometimes referred to as Laser Metal Deposition (LMD), is a welding technology in which a laser forms a melt pool on a metallic parts’ surface. At the same time a powder feedstock is blown through a nozzle into the process zone, where it is preheated by the laser and then absorbed by the melt pool. After solidifying, raised welding beads remain. By repeating the process, the welding beads are built on top of each other and a three-dimensional structure is formed. Powder Laser Energy Deposition is a sub-group of the Direct Energy Deposition technologies. Typical for DED technologies is the high deposition rate of material, which is locally applied to form near net-shape blanks.
Processing unit with multi axis system
The laser beam and the powder supply are combined in a single processing unit, the working head. In a multi axis system typically the working head as well as the substrate plate on which the part is build are fixed to some kind of motion system. The supplier BEAM uses a gantry with five continuous axes for realization of the processing unit’s motion. TRUMPF offers Powder Laser Deposition systems in which the processing unit head is attached to a robot arm. For rotationally symmetric parts, substrate plates can also be fixed to a rotation-tilt table.
Hybrid Powder Laser Deposition technology
In a hybrid system, such as from supplier DMG MORI, the Powder Laser Deposition process is combined with a subsequent CNC machining. The build platform is movable around two axes and the process unit head around three axes. After a section of part or the complete part is built, a milling head is extended and finishes the as-printed parts’ surfaces.
Read more about this topic in the Metal Technologies Course.